|

According to Inside US Trade, ![]() in the third round the NAFTA renegotiation (September 23-27, 2017), the United States has put forward several possible changes to the existing rules related to textile and apparel in the agreement:
in the third round the NAFTA renegotiation (September 23-27, 2017), the United States has put forward several possible changes to the existing rules related to textile and apparel in the agreement:
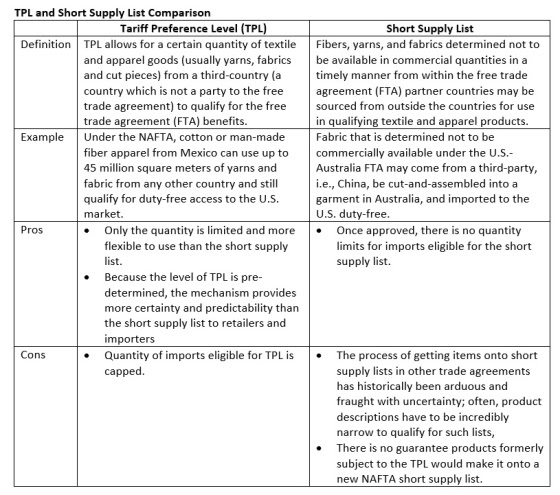
- USTR proposes to eliminate the tariff preference level (TPL) in NAFTA. The goal of eliminating TPL is to limit the exceptions to the yarn-forward rules of origin and “incentivize” more production in the NAFTA region as advocated by the U.S. textile industry.
- As a potential replacement for TPL, USTR also proses to add a short supply list mechanism to NAFTA, but details remain unclear (e.g., whether the list will be temporary or permanent; the application process).
- USTR further proposes a new chapter devoted to textile and apparel in NAFTAin line with more recent agreements negotiated by the U.S.. The current NAFTA does not include a textile chapter.
USTR’s proposal to remove TPL in NAFTA has met strong opposition by the ![]() U.S. apparel industry, fashion retailers, and brands as well as their partners in Mexico and Canada. According to these industry groups:
U.S. apparel industry, fashion retailers, and brands as well as their partners in Mexico and Canada. According to these industry groups:
- Eliminating TPLs would disrupt supply chains that have been in place for more than two decades.
- Eliminating TPLs would not siphon Chinese production back to the U.S. but would instead further incentivize sourcing from outside the NAFTA region and put textile and apparel factories in the region out of business. This is because certain yarns, for example, are not produced in the region but can be produced inexpensively outside of it and imported through a TPL to the NAFTA region, where it could be used in a finished product that would still be considered originating.
- Without the TPL, companies would opt to produce textile and apparel products in the least expensive way possible, likely outside the NAFTA region, and ship items into North America despite being hit with most-favored-nation (MFN) tariffs.
- A short supply list would not ease the supply chain disruptions that would result from the removal of the TPLs because there is no guarantee products formerly subject to the TPL would make it onto a new NAFTA short supply list.
A potential compromise could involve a reduction in Canadian and Mexican TPLs to the U.S. and an increase in the U.S. TPLs to Mexico and Canada, which could boost the U.S. trade surplus in textiles and apparel with its NAFTA partners and throw a bone to the U.S. textile industry by ostensibly incentivizing domestic production.
Fact-check about TPL
TPL was included in NAFTA as a compromise for adopting the yarn-forward rules of origin in the agreement. Before NAFTA, the US-Canada trade agreement adopted the less restrictive fabric-forward rules of origin.
The TPL mechanism has played a critical role in facilitating the textile and apparel (T&A) trade and production collaboration between the United States and Canada, in particular, the export of Canada’s wool suits to the United States and the U.S. cotton or man-made fiber apparel to Canada. Statistics from the ![]() Office of Textiles and Apparel (OTEXA) show that in 2016 more than 70% of the value of Canada’s apparel exports to the United States under NAFTA utilized the TPL provision, including almost all wool apparel products. Over the same period, the TPL fulfillment rate for U.S. cotton or man-made fiber apparel exports to Canada reached 100%, suggesting a high utilization of the TPL mechanism by U.S. apparel firms too (
Office of Textiles and Apparel (OTEXA) show that in 2016 more than 70% of the value of Canada’s apparel exports to the United States under NAFTA utilized the TPL provision, including almost all wool apparel products. Over the same period, the TPL fulfillment rate for U.S. cotton or man-made fiber apparel exports to Canada reached 100%, suggesting a high utilization of the TPL mechanism by U.S. apparel firms too (![]() Global Affairs Canada, 2017). Several studies argue that without the TPL mechanism, the U.S.-Canada bilateral T&A trade volume could be in much smaller scale (
Global Affairs Canada, 2017). Several studies argue that without the TPL mechanism, the U.S.-Canada bilateral T&A trade volume could be in much smaller scale (![]() USITC, 2016). Notably, garments assembled in the United States and Canada often contained non-NAFTA originating textile inputs, which failed them to meet the “yarn-forward” rules of origin typically required for the preferential duty treatment under NAFTA.
USITC, 2016). Notably, garments assembled in the United States and Canada often contained non-NAFTA originating textile inputs, which failed them to meet the “yarn-forward” rules of origin typically required for the preferential duty treatment under NAFTA.
Leave a comment